In a recent article I wrote extensively about the benefits of Zinc. This basic mineral is a basic building block of our bodies, that helps us synthesize protein, produce testosterone, and even unlocks our DNA.
Which got one reader a bit worried about Zinc deficiency. After all, it stands to reason that if Zinc provides all those benefits, then there are probably stark consequences if we don’t get enough. And that’s absolutely true. First we’ll look at some short-term signs you may be Zinc deficient, then look at what the long-term effects might be. Then we’ll explore which people might be most at-risk, and what we can all do to stay safe.
What You Need to Know:
Most Common Signs of Zinc Deficiency
It’s important to know what the symptoms are of malnutrition, but many signs can point to multiple issues. So we not only need to know what it looks like if you’re low on Zinc, but we need to look at why this is occurring, that way you don’t accidentally overcompensate with too much Zinc and miss the root cause of the symptom.
Here’s the list of symptoms, and below that we’ll look into the mechanisms of what’s going on.
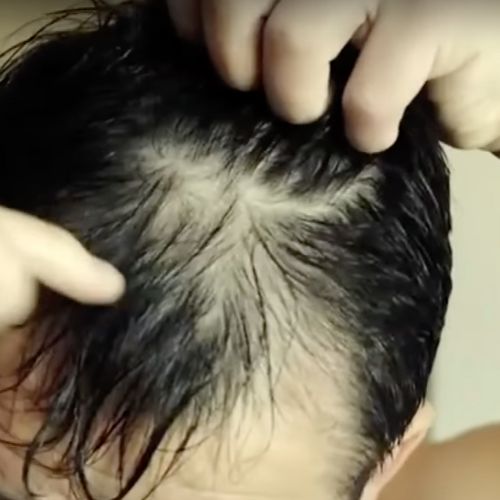
Hair Loss
Because Zinc is required for the action of over 300 enzymes, many of our basic nutrients aren’t absorbed without it. Because of this and its ability to help us metabolize proteins, Zinc is necessary for hair growth. So necessary, even, that one study on alopecia (hair loss), concluded that “Zinc supplementation needs to be given” to people with hair loss.
Diarrhea
Again, this comes down to digestion. Without Zinc, our entire GI (gastrointestinal) tract is thrown out of order. And Zinc-caused diarrhea is a feedback loop–the more we have diarrhea, the lower our Zinc, the more diarrhea we suffer from. In one study, this unseemly affliction was reduced by 39% with Zinc supplementation.
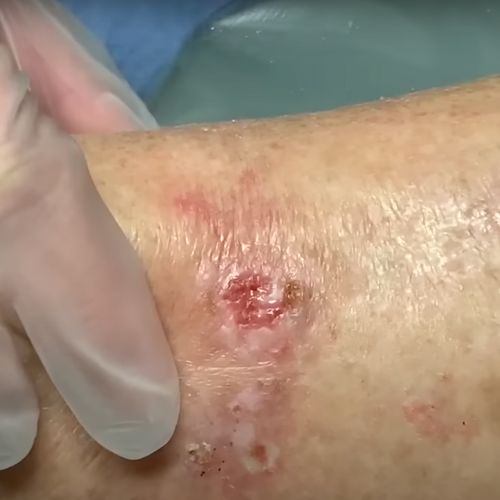
Infections and Wounds
In my previous article we discussed how Zinc is the most important mineral for our Immune System. Because it’s heavily involved in making and using proteins, our bodies cannot heal without it. And while we’re not healing, we’re more at risk of infection, infections which we can’t fight without Zinc.
Long Colds
Since we’re on the subject of the Immune System, we should point out that if your cold or seasonal flu is lasting longer than normal, it may be due to Zinc deficiency. And adding a Zinc supplement could shorten your cold.
Loss of Appetite
Zinc plays a pivotal role in how our body uses and processes Ghrelin, the hunger hormone. In one study, researchers found that children with low Zinc levels also had impaired Ghrelin response. In a laboratory trial, Japanese researchers discovered that withholding Zinc from animals suppressed their appetite.
Loss of Testosterone
As we discussed in our Zinc-Testosterone article, this mineral is essential to male health and performance. A study of 720 men showed a direct relationship between Zinc and Testosterone levels. Not something to be taken lightly.

Mouth Sores
Because of its effects on our Immune System, lacking Zinc can lead to a recurrence of some otherwise minor irritations. For instance, 28% of people with recurring mouth sores had Zinc deficiencies, making this a telltale sign you might need more Zinc in your diet if this happens to you.
Loss of Smell and Taste
Though this mechanism isn’t fully clear, one link came up during recent “long-COVID” research. Medical professionals found that among people suffering from loss of smell and/or taste, many also had Zinc deficiencies. It may be related to the body fighting an infection for so long that it burns through its mineral reserves, something we’ll talk about a bit further down.
Cognition
Because Zinc is involved in the cellular transfer of nutrients, and for the transportation of proteins, especially in the brain, without Zinc we can suffer severe cognitive failure, including loss of memory.
Depression
Again, modern science is still exploring the link, but Zinc has been correlated so strongly to depression and anxiety that one research paper supports using it as an adjunct treatment for some symptoms.

Long-Term Consequences
We won’t spend as long on each of these symptoms, as many of them take years to develop and the mechanisms are a direct result of the above symptoms. For instance, lack of protein synthesis over time will of course mean a person doesn’t grow as tall as they could have and later-in-life bone fragility. And depleted Zinc destroys the immune system, leading to long-term infections.
We list these as warning signs. If you’re worried you may have suffered or do suffer from these as a result of Zinc deficiency, seek medical attention as necessary.
People Vulnerable to Zinc Deficiency
The two main reasons someone could be vulnerable to a Zinc deficiency are
a) Diet.
b) Ongoing medical condition.
c) They have a genetic condition.
Diet
Vegetarians and Vegans are the people most at risk of inadequate Zinc because the most common foods that have proper Zinc are animal proteins. The next at risk people are those who drink excessive alcohol, or who have high Copper, Calcium, or Phosphates in their diets. All of those things prevent our bodies from absorbing Zinc, no matter how much we consume.
Ongoing Conditions
There are three ongoing conditions that can impair your body’s ability to maintain Zinc levels. The first is having a child. Both pregnancy and breastfeeding strip the mother’s body of several nutrients, including Zinc. The second condition is any traumatic, wide-spread wounding or burning. Not only is your body trying to fight infections all over the open wound areas, but the toll of rebuilding skin and muscle tissue depletes the rest of your body of its Zinc stores.
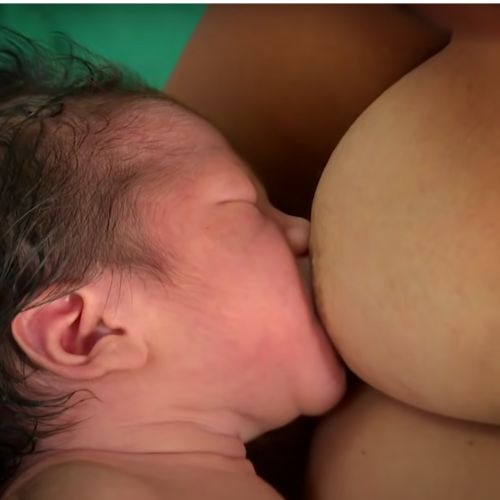
Lastly, Diabetes takes an incredible toll on our Pancreas. And as I wrote in the Benefits of Zinc article, the Pancreas uses a ton of Zinc. Because of this, diabetic people should always monitor their Zinc levels.
Genetic Conditions
There are four conditions that people are typically born with, or that express themselves for genetic reasons later in life, though lifestyle choices can cause them. They are:
If you have any of these conditions, or suspect you might, they can and will cause sever Zinc deficiencies, and you should speak with your doctor about clinical levels of supplementation.
One Last Thing
An outlier that probably doesn’t affect too many people is the use of a common diuretic, hydrochlorothiazide. One study found that taking it robbed men’s bodies of so much Zinc it caused sexual dysfunction. Only men in the study who took 500 mg of Zinc recovered their sexual function.
Where to Get More Zinc
Now the scary stuff is over. Here’s the part where we discuss how to avoid Zinc Deficiencies. Not only should you be aware of the diet and medical conditions listed above, but you should also take active steps to keep you Zinc levels up. The following are the food sources with the highest Zinc concentrations.
And don’t forget that quality supplementation can make a huge difference. Especially if you have chosen a Vegetarian or Vegan diet.
Final Word
Zinc, as we’ve seen, is not only incredibly beneficial as a supplement, and paramount for Testosterone health, but lacking the right amount of Zinc can have devastating consequences. In short, Zinc isn’t a luxury nutrient–it’s necessary for our health and wellbeing. So add it to your diet or supplement routine, and enjoy the peace of mind that comes from knowing you’re giving your body what it needs, so it can give you what you want.
Related Articles:

